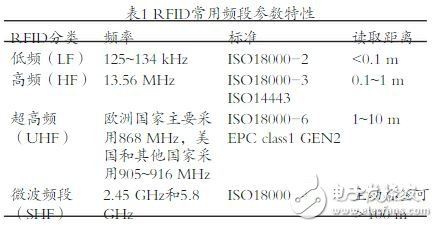
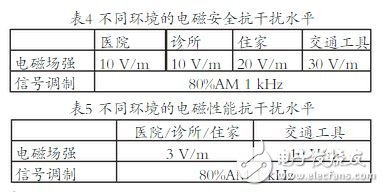
As a fast, accurate and effective identification method, radio frequency identification technology has been widely used in the medical and health industry. This paper explores the potential interference of radio frequency identification (RFID) equipment by analyzing the electromagnetic compatibility standards and related requirements of medical equipment in the medical environment, and proposes measures to reduce interference. Radio Frequency Identification (Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon, RFID) technology has been widely used in the medical and health industry as a fast, accurate and effective identification method. With the rapid development of hospital informationization in recent years, RFID technology has been widely used in hospital personnel tracking management, blood product management, drug management, hospital bed management, consumables and equipment tracking management [1]. On the one hand, it can improve the efficiency of medical staff, on the other hand, it can reduce the occurrence of medical errors and reduce the risk of treatment. 1 Introduction to RFID technology RFID technology is a modern information collection technology and the basis for the development of the Internet of Things. RFID systems typically consist of a reader and a transponder. The reader antenna can read or rewrite the electronic information stored on the tag by transmitting or receiving electromagnetic waves that load the wireless signal. According to different energy supply methods, RFID tags are mainly divided into passive (active), active (AcTIve) and semi-active (Semi AcTIve); according to different operating frequencies, RFID tags are classified into low frequency (LF) and high frequency. (High Frequency, HF), Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Super High Frequency (SHF) tags [2]. In terms of applications, low-frequency and high-frequency electronic tags have a short reading distance and a small amount of data, so they are suitable for close-range recognition. UHF systems have different electromagnetic induction methods, readers and tags can read distances of >10 m and data rates up to 640 kbps. See Table 1 for the characteristics of the commonly used frequency bands of RIFD. 2 RFID electromagnetic interference phenomenon in medical industry applications With the rapid development of hospital information management in recent years, RFID technology has gradually gained favor from the medical industry. It can realize seamless connection with the hospital's existing information system, realize the intelligentization of hospital data collection and effective management of medical behavior. . However, while a new technology brings convenience, it will inevitably bring about unknown problems. There is a risk of Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in electronic medical devices. For the application of RFID devices in the medical environment, China has not yet developed corresponding use standards and specifications, so some scholars question whether it will cause potential electromagnetic interference to normal operating medical devices like mobile phones or other radio transmitting devices. 3]. Relevant research has been carried out abroad. In 2007, Seidman et al. of the US FDA demonstrated that RFID devices can cause certain electromagnetic interference to cardiac pacemakers and implantable cardiac defibrillators [4]. In this report, 71% of low-frequency devices and 11% of high-frequency devices generate interference waves for implantable products. In 2008, Togt et al. of the University of Amsterdam Medical Center in the Netherlands demonstrated that RFID systems can cause different levels of electromagnetic interference to medical devices [5]. The study, conducted in a controlled environment, showed that UHF RFID interfered with 63% of medical devices. Hoelsher et al. at the German Center for Medical Technology and Ergonomics have also experimentally demonstrated that RFID UHF systems can generate electromagnetic fields that exceed safety standards for medical devices [6]. These foreign test studies have proved that existing RFID devices can cause potential electromagnetic interference to medical devices, which affects the normal operation of the device and even threatens the patient's life safety. Therefore, the electromagnetic interference problem of RFID on medical devices is particularly worthy of careful consideration. 3 Electromagnetic compatibility standards in medical environment The RFID signal is transmitted and fed back through electromagnetic waves of different frequency bands, so when it is used in a medical environment, it is necessary to take into account electromagnetic interference that may be generated to the medical device. Electromagnetic interference signals may affect some highly sensitive medical devices and the corresponding diagnostic, treatment and monitoring processes, interfere with or change the treatment parameters, and even cause the device to not function properly, thus affecting the medical effect and causing a negative effect [7]. As far as the medical device itself is concerned, on the one hand, it needs to have certain anti-electromagnetic interference capability, and the other party must be able to collect the smallest information signal. Therefore, the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) test of medical electronic equipment is considered to be an important quality indicator, which mainly includes the Immunity Test and the Emission Test [8]. Electromagnetic immunity to life support equipment and non-living support equipment is specified in IEC 60601-1-2 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 1-2: Safety General Requirements Parallel Standards: Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements and Tests" The anti-interference levels are 10 V/m and 3 V/m [9], respectively. Life support equipment mainly refers to medical equipment that plays a key role in maintaining patient life, such as ventilator and hemodialysis machine. Compared with non-living support equipment, the safety performance requirements of such equipment are more stringent, and the level of anti-electromagnetic interference is higher than that. Non-life support equipment. In IEC61000-4-3 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Part 4-3: Test and Measurement Techniques - Radioactive, Radio Frequency, Electromagnetic Field Immunity Tests, medical equipment is among the electromagnetic compatibility standards for all electrical and electronic equipment. Level 3 and Level 2 [10-11]. Low-frequency interference mainly comes from the interference voltage generated by conducted emissions; while high-frequency interference mainly comes from the electromagnetic interference field strength generated by radiated emissions. At the same time, in the IEC60601-1-2 standard, the recommended distance of anti-interference of medical equipment in electromagnetic environment is also given. Under the same transmitting power, the anti-electromagnetic interference level of life support equipment is higher than that of non-living support equipment. The recommended distance is also relatively long, as shown in Tables 2~3. Note: The ISM band includes 6.765~6.795 MHz, 13.553~13.567 MHz, 26.957~27.283 MHz, 40.66~40.70 MHz, etc. The level of compliance refers to the application of a given electromagnetic interference to a device that is still working properly and Maintain the level of interference strength for the required performance level; rms is the voltage rms value, which is the effective voltage; P is the maximum output power rating of the transmitter provided by the manufacturer. In the IEC60601-1-4 (4th edition) and the IEC medical electrical equipment electromagnetic compatibility and safety work recommendations issued in 2009, the content of anti-electromagnetic interference for medical equipment has been added, among which: Safety Immunity Test Levels and Performance Immunity Test Levels, which stipulate that the safety standards of medical equipment are higher than the performance standards [12], and the existing electromagnetic environment is newly defined and Classification, introduces the method of risk assessment of ISO14971 "Application of Risk Management to Medical Devices". These new additions are designed to ensure that wireless devices can be used more securely and efficiently in a healthcare environment. 4 Electromagnetic compatibility in different medical environments In the past standards for anti-electromagnetic interference of medical devices, only the use of medical equipment in hospitals was often considered. However, with the development of technology, many devices have become lighter and more convenient, and are convenient for patients to use in various locations, especially portable, implantable and wearable medical devices. For example, implantable pacemakers must be able to work properly and safely in a variety of locations without being disturbed by other electronic signals or devices. Therefore IEC60601-1-4 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 1-4: General Requirements for Basic Safety and Necessary Performance: Testing and Requirements for Electromagnetic Interference", proposes the classification of electromagnetic environment and how to reasonably determine the level of anti-interference according to the environment. . In this version of the standard, different electromagnetic environments are emphasized, namely hospitals, clinics, homes, and vehicles [12]. The anti-interference levels required for medical devices in different environments are shown in Tables 4-5. 5 Discussion This paper analyzes the existing electromagnetic compatibility standards of the medical industry, points out that RFID has potential electromagnetic interference to medical equipment, and points out that the requirements for anti-electromagnetic interference in different medical environments are different. Therefore, in the intensive care unit, operating room and other similar medical environments, the implementation of RFID technology requires on-site electromagnetic interference testing according to relevant standards [13-15]. In the implementation process, CISPR 11 "Industrial, Scientific and Medical Equipment - Radio Frequency Interference Characteristics - Measurement Limits and Methods" or ANSI C63.18 "Evaluation of Field Tests for Evaluation of Medical Equipment's Radiated Electromagnetic Immunity to Specific RF Transmitters The method measures the degree of electromagnetic interference in different environments and conducts related equipment risk assessment through ISO14917 "Application of Medical Device Risk Management to Medical Devices". At the market level, RFID device manufacturers have gradually paid more attention to their market in the medical industry. Through continuous development of technology, RFID devices that are more suitable for use in medical environments will be developed to reduce electromagnetic waves to medical devices while ensuring information transmission. Interference. At the application level, many healthcare organizations have launched different RFID projects. As the hospital's equipment management department, it should assess the environmental risks and ensure the safe use of RFID equipment through the risk management mechanism implemented in the medical environment, mark the risk areas that may be interfered, and take appropriate protective measures to improve the anti-electromagnetic interference of medical equipment. Ability [16]. At the technical management level, relevant institutions and organizations are also required to formulate corresponding industry standards and regulate industry applications so that RFID technology can be applied more securely in the medical environment.
SMD Piezoelectric Buzzers are generally smaller than pin type Piezoelectric Buzzers. They are optimized for small devices such as blood glucose meter, clinical/forehead thermometers, smart glasses, and portable terminals.
From product designing, purchasing and testing, every step is controlled strictly by our QC staffs in order to make sure the perfect quality of our products. Currently, over 70% products are exported to US. South East Asia and Europe.
Smd Piezo Buzzer,Piezo Passive Smd Buzzer,Portable Micro Alarm Buzzer,Passive Micro Smt Alarm Buzzer Jiangsu Huawha Electronices Co.,Ltd , https://www.hnbuzzer.com