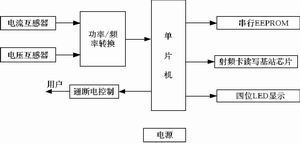
Pick  Essentials: This article introduces a digital prepaid meter system based on a radio frequency card, and gives the hardware and software structure of the digital meter. introduction The radio frequency card is a non-contact smart IC card. It is a new technology developed in recent years. It transmits data through radio waves without the electrical contacts of the contact IC card. Therefore, compared with the traditional The contact IC card has the advantages of high reliability and long life, and has been widely used. We use ATMEL 's TEMIC series 125kHz radio frequency card read and write base station chip U2270B to design prepaid digital watt-hour meters. System composition The whole system is composed of three parts: the meter management system, the radio frequency card, and the radio frequency card prepaid digital electric meter. The electricity meter management system is used by the electricity management department to issue electricity meter radio frequency cards to users, user electricity purchase writing cards, and user electricity purchase information management. The system consists of a microcomputer, meter management software, and meter dedicated radio frequency card reading and writing equipment. The functions it completes are: the initialization of the meter radio frequency card, which can set, clear, and change the password, write the user's pre-purchased power into the user card, and write the user's newly purchased power into the database. The maintenance of the meter radio frequency card database includes querying, deleting, transferring and printing. The radio frequency card is used to record information such as the user's serial number, the pre-purchased power and the working parameters of the power meter. The prepaid electricity meter supplies power to the user according to the power pre-purchased by the user, and accurately records the user's power consumption, and sends an alarm message when the power pre-purchased by the user is about to run out. If the user does not purchase electricity again within the specified power consumption range The meter will automatically cut off the user's power supply and will not resume power supply until the pre-purchased power is written into the radio frequency card again and confirmed. Figure 1 Radio frequency card reading and writing circuit diagram  Picture 2 Block Diagram of Electricity Meter The hardware composition of the radio frequency reading and writing system There EEPROM 264bit in series TEMIC RF card, it is divided into 8 (block). In block 8, Block0 is a control block for controlling the various operating characteristics of the card, such as: synchronization signal, coding, baud rate, data stream length, and the encrypted passwords off function enabled wake-up and the like; block1 ~ bloc6 It is a user block, used to store user data and information; block7 is a cipher block, if the encryption function is not enabled, it can also be used as a user block. This system sets the base station to work at 125kHz carrier frequency, uses RF/32 transmission baud rate, Manchester encoding, uses Sequence Terminator synchronization signal, and cyclically sends block1~block6 data. In this working mode configuration, the bit clock cycle ms = 256ms . This system selects AT89S52 single-chip microcomputer as the main control module, and forms a TEMIC series radio frequency card reader system together with TEMIC series radio frequency card reading and writing module, serial communication module and sound and light prompt circuit . The system hardware circuit is shown as in Fig. 1 . The base station antenna needs to be circumvented by the user. Generally, copper enameled wire can be wound with a diameter of 3cm and 150 turns, and the inductance value is 1.35mH . The carrier frequency fosc is typically 125kHz , and it can also be set by the user. This frequency is determined by the value of the current flowing into the RF(15) pin, so by adjusting the value of the current limiting resistors Rf1 and Rf2 between the RF(15) and VS(14) pins, this frequency can be changed. The specific Calculated as follows: Rf1+Rf2=k Ω When fosc=125kHz , Rf1 + Rf2=110k Ω. What the base station reads from the radio frequency card is the 125kHz carrier modulated signal, which is coupled to the INPUT (4) pin through the CIN capacitor , and after passing through the low-pass filter, amplifier, and Schmitt trigger , it enters the OUTPUT (2) The pin outputs the demodulated signal. The cut-off frequency of the low-pass filter is determined by fosc , generally fosc/18 . The value of the coupling capacitor CIN of the INPUT pin and the decoupling capacitor CHP of the HIPASS(16) pin determines the high-pass characteristics of the demodulation circuit, which is beneficial to further eliminate interference signals. The values ​​of CIN and CHP are different according to the data transmission baud rate of the radio frequency card. The baud rate is 680pF and 100nF respectively under fosc/32 . The relationship between CHP and lower cutoff frequency is as follows: Ri=2.5k Ω. It should be noted that the signal output by the OUTPUT pin is only demodulated and not decoded. The decoding task must be completed by the microcontroller programming. Hardware structure and software of prepaid meter Figure 2 is a schematic block diagram of a digital radio frequency card prepaid meter. The meter head circuit uses the high-precision electric energy metering chip AD7755 , which uses pulse output to measure electricity. In AD7755 , only the A/D converter and reference circuit use analog circuits, and all other signal processing ( such as multiplication and filtering ) use digital circuits to ensure stability and accuracy under various extreme environmental conditions. The device has the following characteristics: high precision, support 50/60HZ International Electrotechnical Commission 521/1036 standard, within a dynamic range of 500: l error is less than 0.1% ; AD7755 provides average real power at the frequency output terminals F1 and F2 ; high-rated output CF provides instant power, which can be interfaced to MCU ; programmable gain amplifier in current channel facilitates interface with sensor; on-chip power supply monitoring. After the pulse output of the CF end of the meter head is photo-isolated, it is connected to the I/O port of the single-chip microcomputer . Its interface circuit is shown as in Fig. 3 . The display part is displayed by a 4 -digit LED digital display tube, which adopts a dynamic display mode. The four LEDs light up in turn, each of them stays for 1ms , and it lights up again after 10ms and repeats. In order to extend the use of LEDs , the display and control of the digital display tube are directly driven by the I/O port of the single-chip microcomputer . The circuit of the radio frequency card reading and writing part is basically the same as the above-mentioned radio frequency card reader and writer of the electricity sales system. The user's power cut-off circuit adopts a magnetic latching relay and its drive circuit, which is turned on and off by the IO port of the single-chip microcomputer, and the misoperation rate of this circuit is extremely low. The power supply circuit is divided into two circuits, one is for the meter head and the other is for the microcontroller and its controlled circuits. They are obtained from 220V alternating current through voltage transformation, rectification, filtering, and voltage stabilization. The two power sources are independent of each other and do not share the same ground. . Figure 3 Meter interface circuit Picture 4 Main monitoring program flow chart Figure 4 is the main monitoring program flow. When the system is powered on and reset and initialized, first read the password, power and other data in the meter data memory EEPROM , and realize the following functions: When the meter is working, as long as an external interrupt occurs, the external interrupt service routine will be executed immediately. The interrupt service program completes the pulse counting function, that is, the power consumption metering function. Each time the interrupt is entered, the software pulse counter is incremented by 1 , and when the count value reaches the standard count value, the power deduction flag is set, and then the interrupt program is exited. After the main monitoring program finds that the power deduction sign is set, it will deduct the power consumption from the total power consumption. Concluding remarks The digital radio frequency card prepaid meter system introduced in this article is designed in strict accordance with the requirements of productization. It uses the high-precision electric energy metering chip AD7755 as the electric energy measurement unit. The system circuit is simple and economical. This system has been practically used in a non-contact IC card prepaid electricity meter sales system in Wenzhou . The practical application shows that the system can meet the design requirements in terms of accuracy and reliability, and the system runs well and has high reliability. . Waveguide Attenuator,Adjustable Rf Attenuator,Waveguide Variable Attenuator,High Power Variable Attenuator Chengdu Zysen Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.zysenmw.com